PART2The principle of a ammeter, voltmeter, Ohm-Meter
Experiment 2 :Ammeter and measurement of current (DC CURRENT METER)
Theory
Shunt
A Shunt is a kind of resistor used to extend the current span by being connected to an ammeter in parallel. For example, when you try to extend the span up to 100mA by using the ammeter that can measure up to 1mA, you only need to make current of 1mA flow through an ammeter and the remaining current of 99mA through a Shunt of current of 100mA.
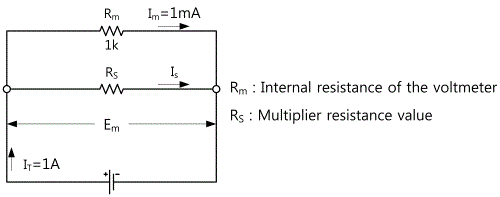
When extending the current span by using a Shunt In the Fig. 2-5, assume that an ammeter's internal resistance is Rm, the current flowing through Rm, RS is respectively Im, IS. If the current to be measured is N-times more than the FS(Full Scale) current of a Current Meter, the Shunt's resistance RS can be calculated as follows. First of all, assuming that a Meter's FS input voltage is Em, the current flowing through Rm, RS, can be respectively expressed as Im=Em/Rm,, IS=Em/RS. Accordingly, the circuit current that can be measured by connecting RS in parallel will become N-times more than the case that the only ammeter is connected.
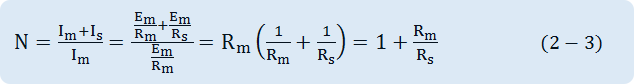
If the current value to be measured is N-times more than Im from the above formula, the Shunt's resistance RS is as below.
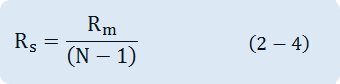
Thus, if you know the maximum span(FS sensitivity) of a Meter and internal resistance, you can design the Shunt based on the range of current to be measured.
If you measure 1A by using the ammeter with 1kΩ of the internal resistance(Rm) and 1mA of span, how much is the Shunt's resistance?
Ammeter
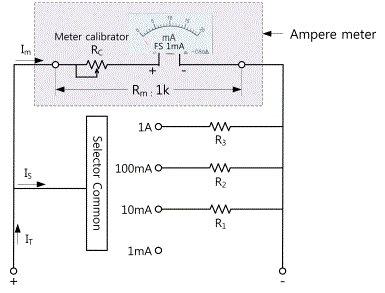
Generally, an ammeter is composed of a Meter and a Shunt connected to a Meter in parallel. In this case, a Meter's sensitivity ranges from 50μA~1mA(FS) and the internal resistance is approximately 100Ω ~ 1kΩ. (The less Rm is, the better under the same current sensitivity) In addition, the Shunt used for measuring high current displays the output voltage for connecting to a Meter with the capacity(A). Let's figure out the principle of an ammeter from the Fig. 2-5. Assuming that input current is IT, the current flowing through an ammeter is Im, the current flowing through a Shunt is IS, IT = Im + IS. In addition, assuming that an ammeter's internal resistance is Rm, a Shunt's resistance is RS, Im and IS will have the below interaction formula.
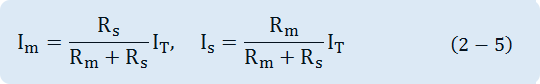
Accordingly, when an ammeter indicates the Im value, the actual current value can be obtained by multiplying magnification of the range.
Exercise 2-4
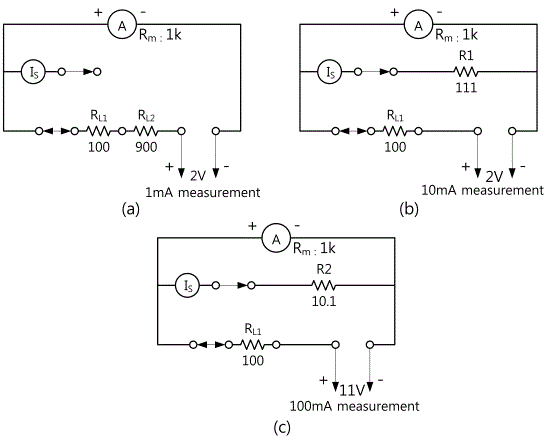
Assuming that the Range is set as 100mA and Rs is 10.1Ω, input current is respectively 100mA and 50mA calculate the actual value of current(IT) (In this case, Im : current flowing through an ammeter, Is : current flowing through a Shunt)
Experiment Procedures
tab1Experiment 2-2.1 Compose the circuit in the Circuit-3, 2 of M-02 as shown in the Fig. 2-7.
1.Wiring method(Circuit-3, 2 of M-02)
(a) Circuit wiring
1.Circuit wiring
Connect 3a terminal and 3b terminal of the Circuit-3 with a yellow line.
2.Power supply
Connect the com terminal and 3e(-) terminal with 0~10V input of the Circuit-3 to the Variable Power with a black line.
Connect the V1 terminal and 3d(+) terminal of the Circuit-3 to the Variable Power with a red line.
3.Connecting V, A, Ω indicator (In case of using an Analog meter)
Connect 3q terminal of the Circuit-3 and 2a terminal of the Circuit-2 with a red line.
Connect 3r terminal of the Circuit-3 and 2c terminal of the Circuit-2 with a black line.
4.Connecting a voltmeter
Connect 3d terminal of the Circuit-3 and A+ terminal of the face panel Signal Input with a red line.
Connect 3e(-) terminal of the Circuit-3 and A- terminal of the face panel Signal Input with a black line
5.Connecting an ammeter
Connect 3f terminal of the Circuit-3 and mA/A terminal of the face panel Multimeter with a red line.
Connect 3g(-) terminal of the Circuit-3 and Low terminal of the face panel Multimeter with a black line.
(b) Circuit wiring
1.circuit wiring
Connect 3a terminal and 3b terminal of the Circuit-3 with a yellow line.
Connect 3i terminal and 3m terminal of the Circuit-3 with a yellow line.
2.Power supply
Connect the com terminal and 3e(-) terminal with 0~10V input of the Circuit-3 to the Variable Power with a black line.
Connect the V1 terminal and 3c terminal of the Circuit-3 to the Variable Power with a red line
3.The connections of V, A, Ω indicator, voltmeter and ammeter are the same as [(a) circuit wiring] 3), 4), 5).
(c) Circuit wiring
1.circuit wiring
Connect 3a terminal and 3b terminal of the Circuit-3 with a yellow line.
Connect 3i terminal and 3m terminal of the Circuit-3 with a yellow line
2.Power supply
Connect the com terminal and 3e(-) terminal with 0~10V input of the Circuit-3 to the Variable Power with a black line.
Connect the V1 terminal and 3c terminal of Circuit-3 to the Variable Power with a red line.
3.The connections of V, A, Ω indicator, voltmeter and ammeter are the same as [(a) circuit wiring] 3), 4), 5).
2.Wiring Diagram
(a) Circuit wiring
(b) Circuit wiring
(c) Circuit wiring
3.Measurement
(a) Circuit measurement
- 1Select variable power on the left menu of the Touch LCD panel.
- 2Select the 3 CH DC tab and click in the DC Voltage V1 to set as 2V. Then, if you click , the output of DC 2V will be input to the circuit
- 3After selecting analog input on the left menu, check the measured voltage of the Volt & Ampere Meter CH A.
After selecting the Volt & Ampere Meter tab on the main screen, click of CH A and click and in Function.
There may be some errors in low output voltage and measured values.
- 4Check whether the FS is 1mA in the V, A, Ω indicator.
(b) Circuit measurement
- 1Wire in accordance with [(b) circuit wiring] of Wiring Method.
- 2Select variable power on the left menu of the Touch LCD panel
- 3Select the 3 CH DC tab and click in the DC Voltage V1 to set as 2V. Then, if you click , the output of DC 2V will be input to the circuit.
- 4After selecting analog input on the left menu of the Touch LCD panel, check the measured voltage of CH A in a Volt & Ampere Meter
After selecting the Volt & Ampere Meter tab on the main screen, click of CH A and click and in Function
There may be some errors in low output voltage and measured values.
- 5If you click dmm on the left menu of the Touch LCD panel, the Digital Multi Meter screen will pop on. At this time, click and record the measured Shunt current(Is) and values of V, A, Ω indicator in the relevant column of the Table 2-3.
- 6How to measure the resistance of a Shunt
Interrupt the output of DC 2V by clicking on the variable power screen and remove the power cable connected to 3c, 3e of the Circuit-3. In addition, remove the yellow line connecting between terminal 3j and 3n.
Select dmm on the left menu of the Touch LCD panel.
Click on the Digital Multi Meter screen and connect terminal 3n of Circuit-3 to the Multimeter High terminal of a face panel. After connecting terminal 3p and the Multimeter Low terminal of the face panel, record the resistance value measured by a Shunt in the Table 2-4.
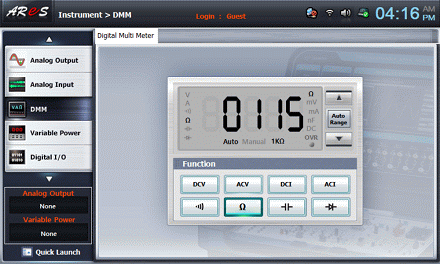
(c) Circuit measurement
- 1Wire in accordance with [(b) circuit wiring] of Wiring Method.
- 2Select variable power on the left menu of the Touch LCD panl
- 3Select the 3 CH DC tab and click in the DC Voltage V1 to set as 11V. Then, if you click , the output of DC 11V will be input to the circuit.
- 4After selecting analog input on the left menu, check the measured voltage of CH A in a Volt & Ampere Meter
After selecting the Volt & Ampere Meter tab on the main screen, click of CH A and click and in Function
- 5If you click dmm on the left menu of the Touch LCD screen, the Digital Multi Meter screen will pop up. At this time, click and record the values of the Shunt current(Is) and V, A, Ω indicator in the relevant column of the Table 2-3.
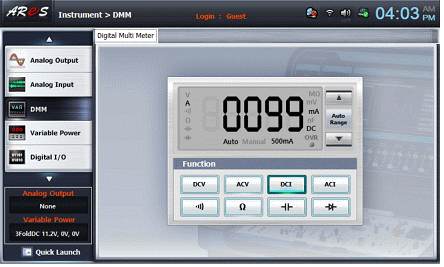
- 6How to measure the resistance of a Shunt
Interrupt the output of DC 2V by clicking on the variable power screen and remove the power cable connected to 3c, 3e of the Circuit-3. In addition, remove the yellow line connecting between terminal 3i and 3m.
Select dmm on the left menu of the Touch LCD panel.
Click on the Digital Multi Meter screen and connect terminal 3m of Circuit-3 to the Multimeter High terminal of a face panel. After connecting terminal 3p and the Multimeter Low terminal of the face panel, record the resistance value measured by a Shunt in the Table 2-4.